bigpigeon.us webpage WWII Japan > Japan Ascendant, © 2024 by Robert A. Christiansen, updated by RAC 16 Feb 2024.
This historical webpage provides context for the 1941-1945 War with Japan.
This historical webpage provides context for the 1941-1945 War with Japan.
- Part 1 - The Growth of the Japanese Empire to 1936.
- Part 2 - The Second Sino-Japanese War.
- Part 3 - The Pacific Islands.
- Part 4 - Southeast Asia in 1941.
- Part 5 - Prelude to the War with Japan, 1939 - 1941.
Part 1 - The Growth of the Japanese Empire to 1936
|
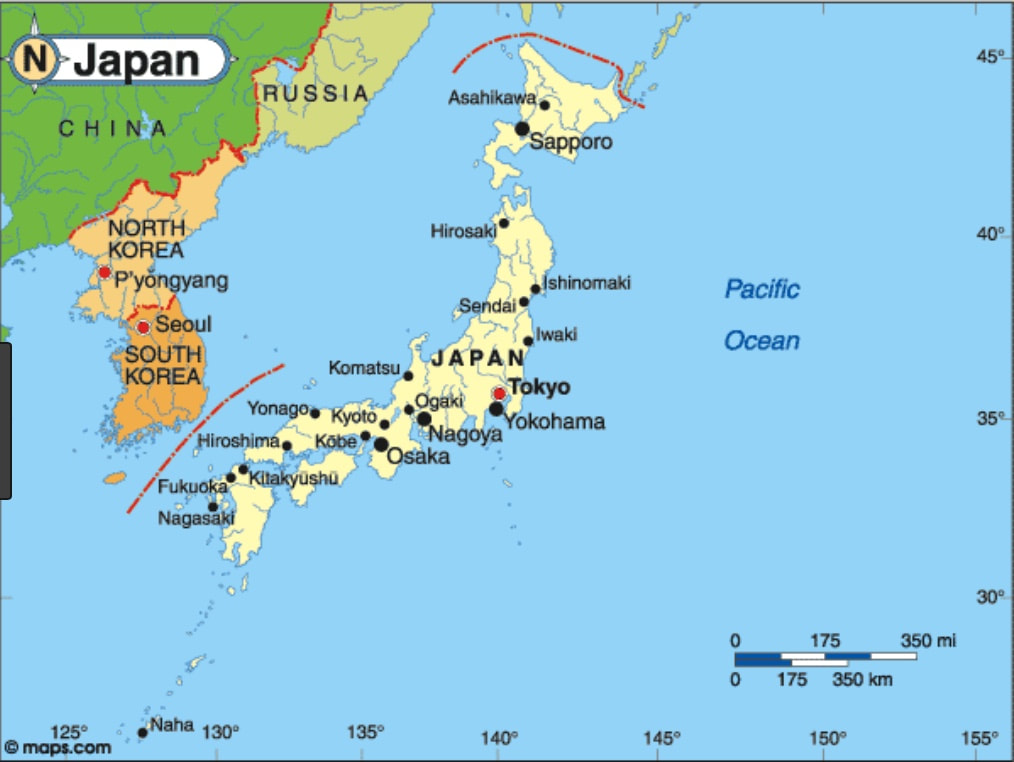
Well into the 1800s, the island nation of Japan had remained aloof from Western influences. Until 1854, Japan allowed foreign trade only through the port city of Nagasaki on the west coast of the south Japanese island of Kyushu. In 1853-54, gunboat diplomacy by Commodore Matthew C. Perry of the United States Navy led Japan to relax trading regulations. Japan soon began adopting with vigor both western technology and expansionist territorial views.
|
|
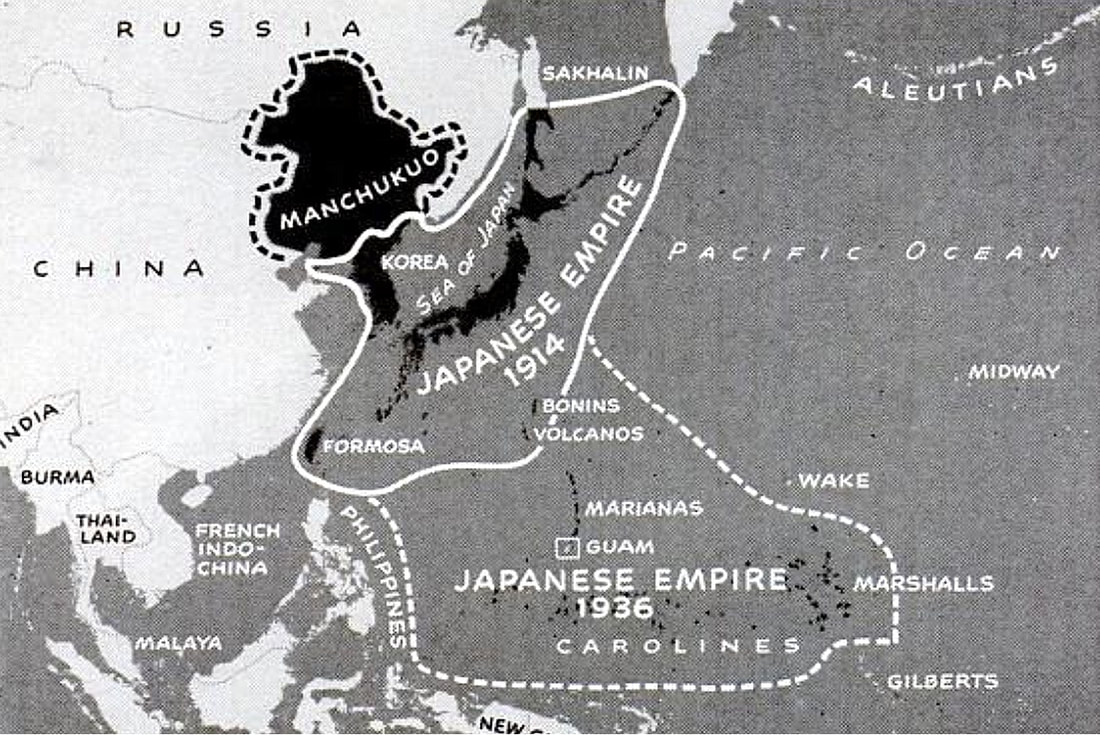
Japanese Expansion to 1936:
|
Part 2 - The Second Sino-Japanese War
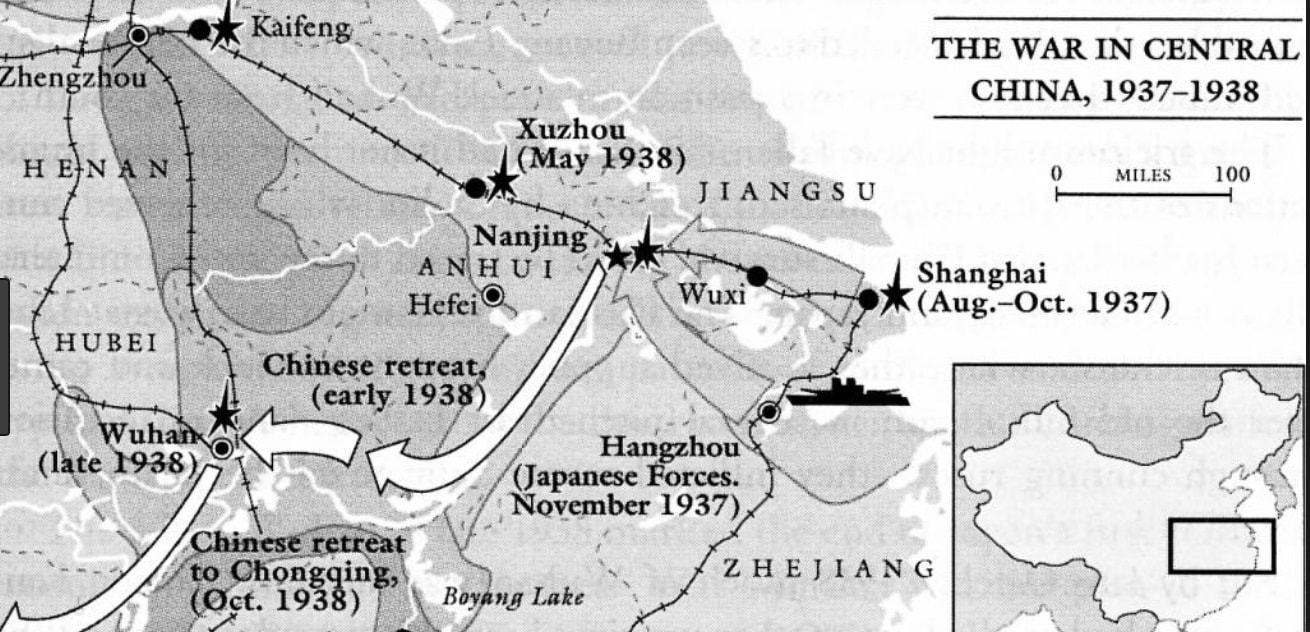
In 1937, the Japanese Empire fabricated a pretext for invading China. This was the beginning of the Second Sino-Japanese War, which after Pearl Harbor sequed into the China-Burma-India Theater of the War with Japan.
|
By the end of 1938, Chiang Kai-shek's Republic of China government had been forced to flee the capital of Nanjing/Nanking in central China and retreat to Chongqing (known in WWII as Chungking) in mountainous southwestern China. There the Republic of China government remained until World War II ended.
Early in the Second Sino-Japanese War, the Imperial Japanese Army (IJA) had also occupied portions of north China, including today's capital of Beijing, and the other major port cities south of Shanghai. |
I end this section with a descriptive quote from a writer far more skilled than me:
"The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937-45) is often relegated to the status of ‘sideshow’, only mentioned to better set the stage for the daring exploits of the British Army in Burma or provide context for the brutal struggles that faced Allied forces in the Pacific during WW2.
"In reality the war for mainland China was so much more: Battles raged from the Great Wall in the north to the humid subtropics of the South China Sea, fought by millions of soldiers of the Imperial Japanese Army, Chiang Kai-Shek’s Nationalists, Mao Zedong’s Communists, and an eclectic assortment of regional Warlords. It was here that the majority of Japan’s war materiel and active divisions were stationed, here where the hardened veterans that devastated Allied forces in the Pacific first saw combat, and here where the fate of modern China was decided."
-- Joe Fonseca, 10 Sep 2018, https://www.wargamer.com/articles/war-games-second-sino-japanese-war/
"The Second Sino-Japanese War (1937-45) is often relegated to the status of ‘sideshow’, only mentioned to better set the stage for the daring exploits of the British Army in Burma or provide context for the brutal struggles that faced Allied forces in the Pacific during WW2.
"In reality the war for mainland China was so much more: Battles raged from the Great Wall in the north to the humid subtropics of the South China Sea, fought by millions of soldiers of the Imperial Japanese Army, Chiang Kai-Shek’s Nationalists, Mao Zedong’s Communists, and an eclectic assortment of regional Warlords. It was here that the majority of Japan’s war materiel and active divisions were stationed, here where the hardened veterans that devastated Allied forces in the Pacific first saw combat, and here where the fate of modern China was decided."
-- Joe Fonseca, 10 Sep 2018, https://www.wargamer.com/articles/war-games-second-sino-japanese-war/
Part 3 - The Pacific Islands
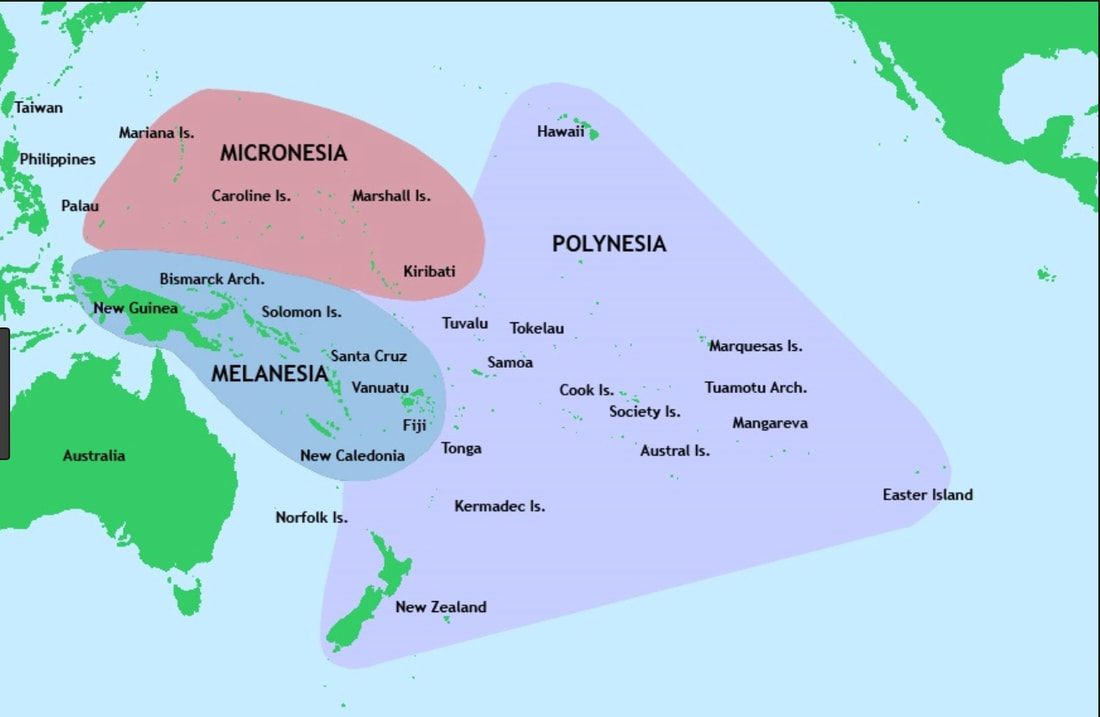
I understood better the War with Japan in the Pacific once I knew the political history of the Pacific Islands shown in the following map, islands on which so many Americans died between 1941 and 1945.
|
For geographical and cultural considerations, these central and south Pacific islands are often divided into three regions as shown here.
For over two years starting in May 1942, most of the the War with Japan in the Pacific was fought first in the regions of Melanesia and then Micronesia. The Pacific War then shifted to the Philippines in October 1944 and to islands south of Japan in February 1945. To the west of these three regions, from south to north, lie the island nations of Australia, Indonesia (formerly the Dutch Indies), The Philippines, Taiwan (formerly Formosa), and Japan. |
Historical Overview of the Pacific Islands:
One hundred years ago, most Pacific islands were politically subordinate to a so-called colonial power. (Sometimes words such as protectorate, territory, or commonwealth were used instead of the word colony.)
The inital European colonial powers, Portugal and Spain, began establishing colonies outside of Europe around 1500. Except for Brazil, Portugal's colonies remained relatively small. Spain, however, soon amassed a massive colonial empire, which included the Philippine Islands and most of Micronesia.
Later England and France also acquired colonial possessions in the Pacific Islands.
In 1871, most German-speaking states of Europe came together as the German Empire, known informally as Germany. Germany soon began acquiring Pacific colonies, especially in northern Melanesia. After the United States defeated Spain in the 1898 Spanish-American War, Germany bought most of Spain's remaining Pacific colonies, including most of Micronesia, while the United States acquired Guam in the Mariana Islands.
One hundred years ago, most Pacific islands were politically subordinate to a so-called colonial power. (Sometimes words such as protectorate, territory, or commonwealth were used instead of the word colony.)
The inital European colonial powers, Portugal and Spain, began establishing colonies outside of Europe around 1500. Except for Brazil, Portugal's colonies remained relatively small. Spain, however, soon amassed a massive colonial empire, which included the Philippine Islands and most of Micronesia.
Later England and France also acquired colonial possessions in the Pacific Islands.
In 1871, most German-speaking states of Europe came together as the German Empire, known informally as Germany. Germany soon began acquiring Pacific colonies, especially in northern Melanesia. After the United States defeated Spain in the 1898 Spanish-American War, Germany bought most of Spain's remaining Pacific colonies, including most of Micronesia, while the United States acquired Guam in the Mariana Islands.
|
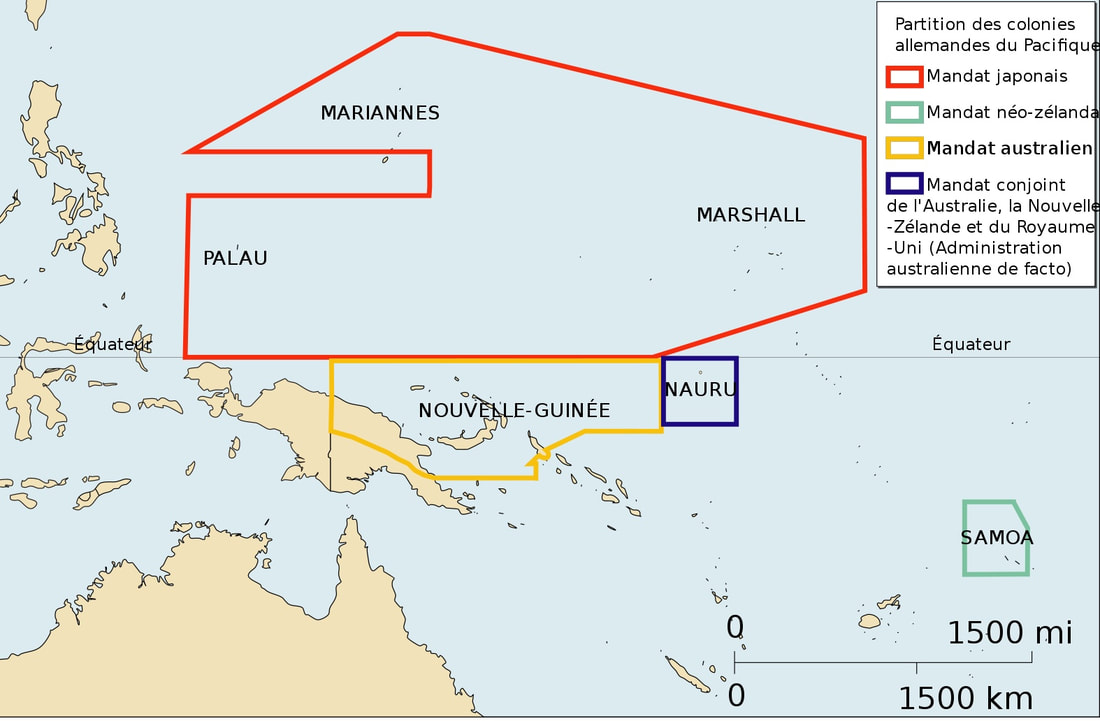
When WWI began in 1914, Japan joined the Allied cause. After the German defeat in 1918, the League of Nations parcelled out portions of the former German colonial empire as so-called mandates among various nations. Japan received the German colonies in Micronesia and Australia received those in northern Melanesia as shown on the accompanying French map.
The League of Nations specified that mandated colonies be demilitarized. However, Japan built infrastructure suitable for military use and brought in thousands of Japanese settlers in its mandates. When Japan launched its multi-pronged attacks in December 1941, some of the attacks came from its mandated territory. |
|
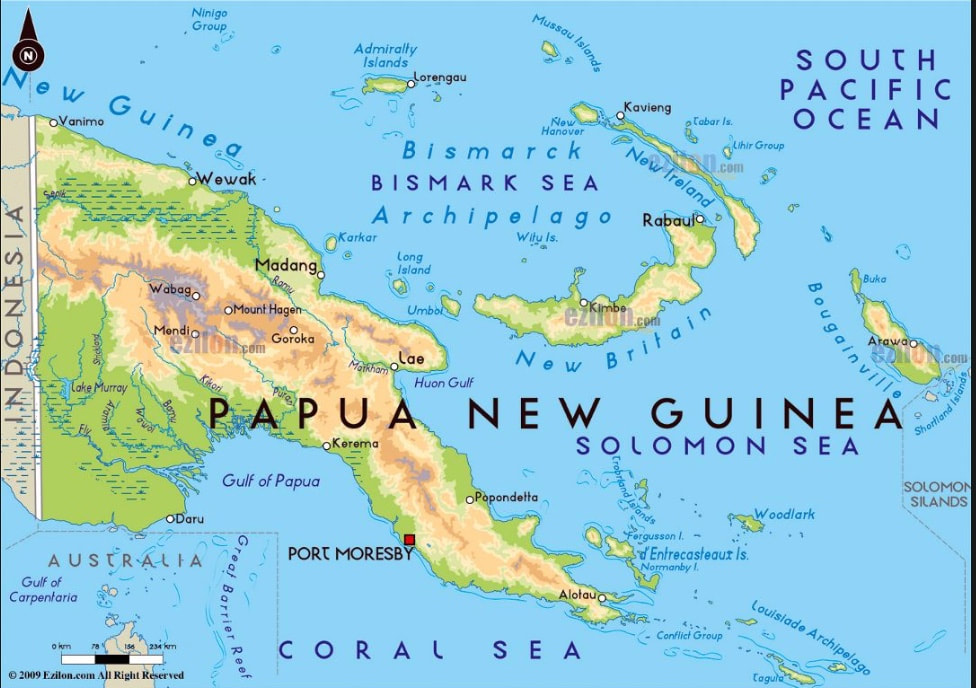
New Guinea in 1941
The large island of New Guinea north of Australia figures prominently in the War with Japan. Today New Guinea has two political parts, with the eastern part appearing on the accompanying map. Back in 1941, New Guinea consisted of three colonial sections as shown on the above map:
|
The Pacific Islands Today:
Today most of Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia is broken up into independent countries. Some, like Hawaii and western New Guinea are part of larger nations. Some colonies remain.
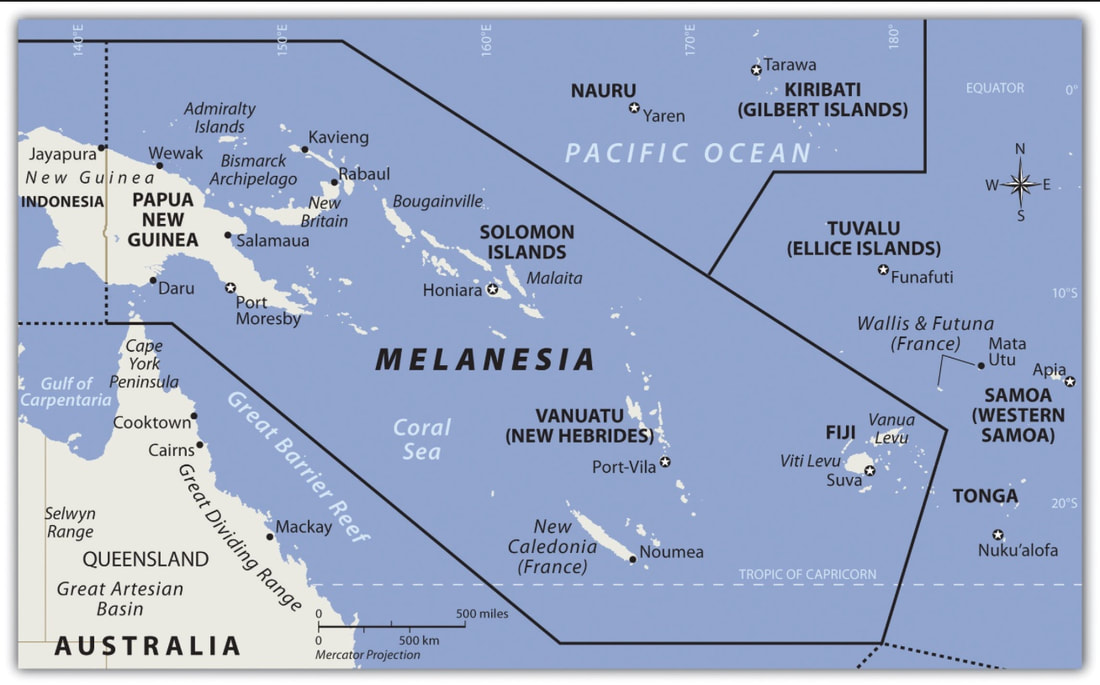
The following map shows today's political organization of Melanesia. The northern part was a major area of US combat in the South and Southwest Pacific theater areas for two years starting in May 1942.
Today most of Melanesia, Micronesia and Polynesia is broken up into independent countries. Some, like Hawaii and western New Guinea are part of larger nations. Some colonies remain.
The following map shows today's political organization of Melanesia. The northern part was a major area of US combat in the South and Southwest Pacific theater areas for two years starting in May 1942.
|
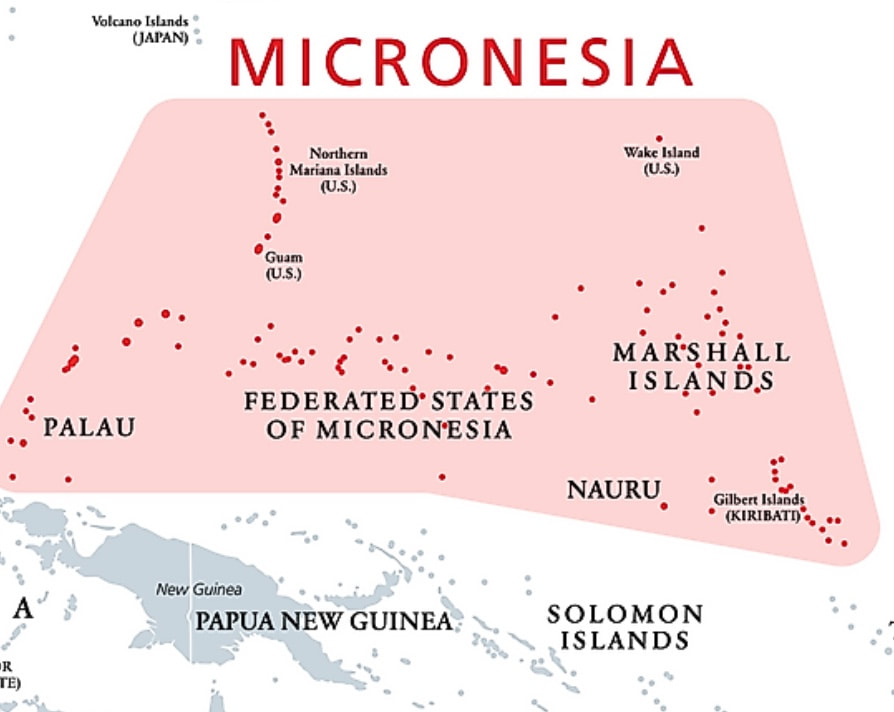
This map shows today's political organization of Micronesia, which was a major area of US combat in the Central Pacific theater area for a year beginnning in November 1943.
|
Except for the Battles of Pearl Harbor and Midway early in the War with Japan, Polynesia did not experience combat.
Part 4 - Southeast Asia
|
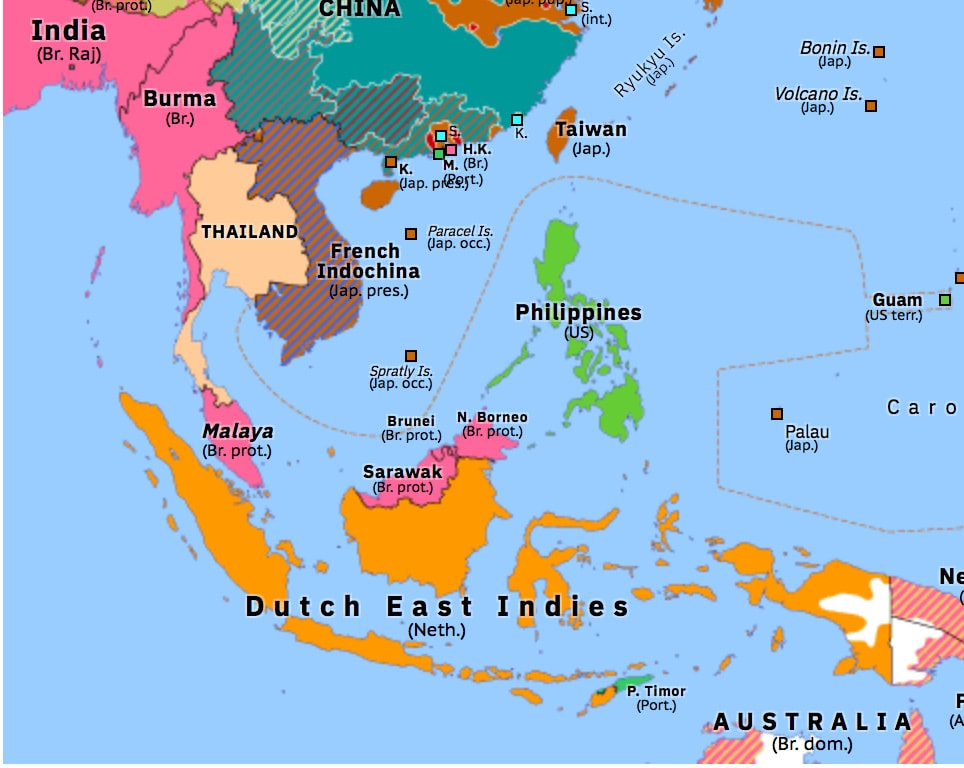
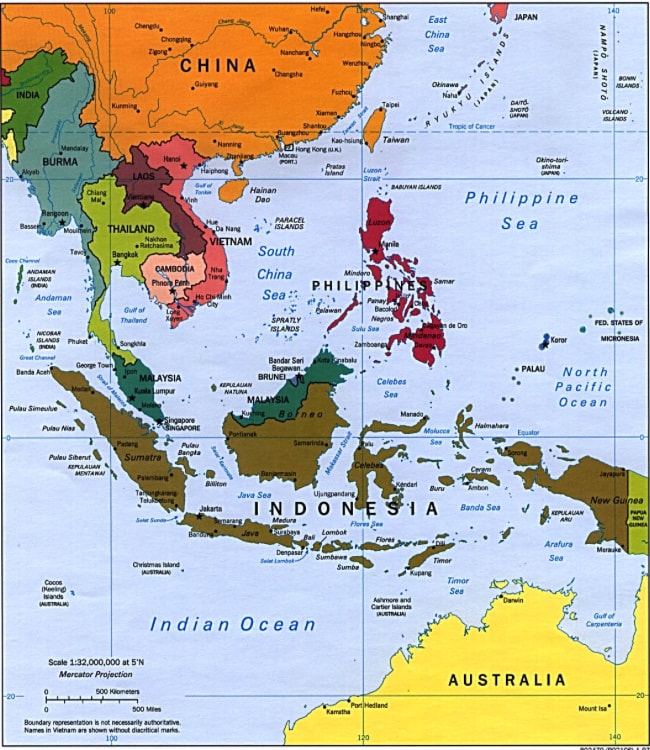
The accompanying maps show the greater Southeast Asia in 1941 and today.
In 1941, Japan coveted access to the natural resources of what is sometimes called the Southern Resources Area, the core of which was the Dutch East Indies and the British colonies in Malaya and on the island of Borneo. Unfortunately, the Philippine Islands, then a United States commonwealth, lay between the Southern Resources Area and the Japanese home islands. |
Part 5 - Prelude to the War with Japan - 1939 - 1941
|
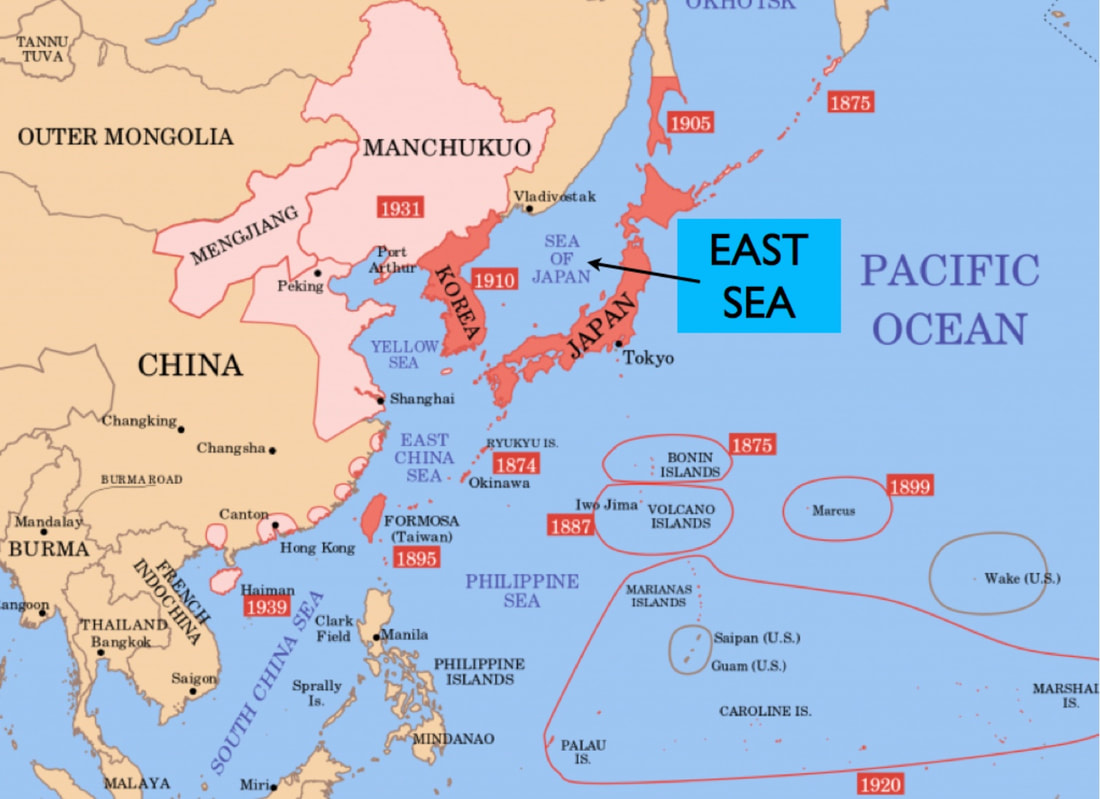
Japan on 1 September 1939
The red areas of the accompanying map shows the extent of Japanese power when The German War, World War II in Europe, broke out with the German invasion of Poland on 1 September 1939. Between that date and the Japanese attacks of December 1941, the following events transpired:
|
Sources for Big Pigeon's WWII Japan > Japan Ascendant webpage:
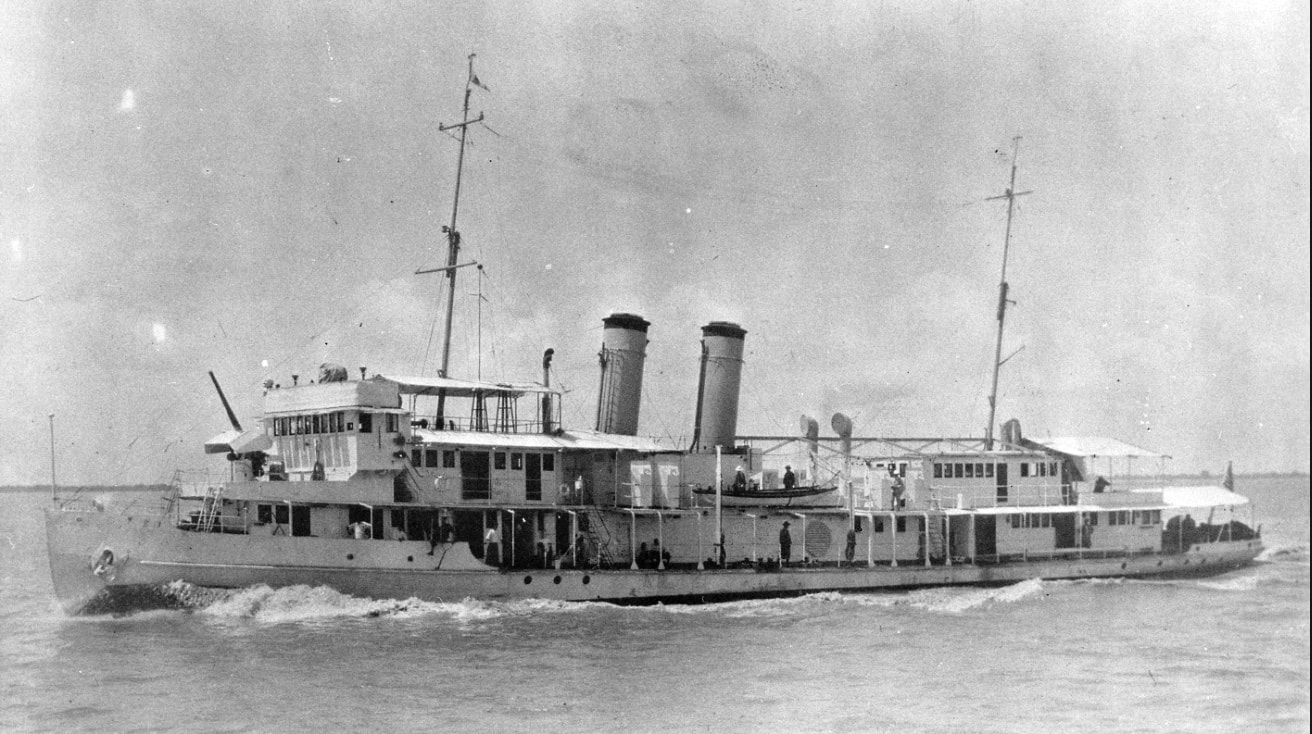
- The webpage header photo shows the USS Panay, an American gunboat, before it was attacked and sunk in the Yangtze River near Nanking by Japanese aircraft on 12 Dec 1937. This incident, and subsequent Japanese atrocities in Nanking, helped turn American public opinion against Japan.
- The Japan and Surrounding Nations map is courtesy of maps.com.
- The Japanese Empire - 1936 map first appeared in the 16 Apr 1945 issue of Life magazine and is courtesy of atlanticsentinel.com.
- The Melanesia, Micronesia, and Polynesia map is courtesy of en.wikipedia.org.
- The Melanesia Today map is courtesy of saylor.org.
- The War in Central China 1937-38 is courtesy of wargamers.com. I don't
- The Japanese Empire - mid 1942 source is currently unknown.
- The The Japanese Empire - 1939 map is courtesy of commons.wikimedia.org.
- The The Japanese War map is courtesy of maps.com.
- The Southeast Asia in 1941 map is courtesy of omniatlas.com and was found at https://omniatlas.com/maps/asia-pacific/19411206/.
- The Southeast Asia Today map is courtesy of the University of Texas Libraries, at https://legacy.lib.utexas.edu/maps/asia.html