bigpigeon.us webpage WWII Germany > The ETO > To the Rhine, © 2023 by Robert A. Christiansen, updated by RAC 26 Dec 2022.
The early 1945 ETO operations summarized herein advanced Allied forces to the left bank of the Rhine River.
The early 1945 ETO operations summarized herein advanced Allied forces to the left bank of the Rhine River.
Links to Big Pigeon's The ETO > To the Rhine webpages:
About the Above Links
|
The following bullets correspond to the above links and summarize European Theater operations during January - March 1945. These operations brought General Eisenhower's seven Allied armies to the left bank of the Rhine River from Basel, Switzerland north to Nijmegen in the Netherlands.
|
The Allied Armies on the Left Bank of the Rhine
|
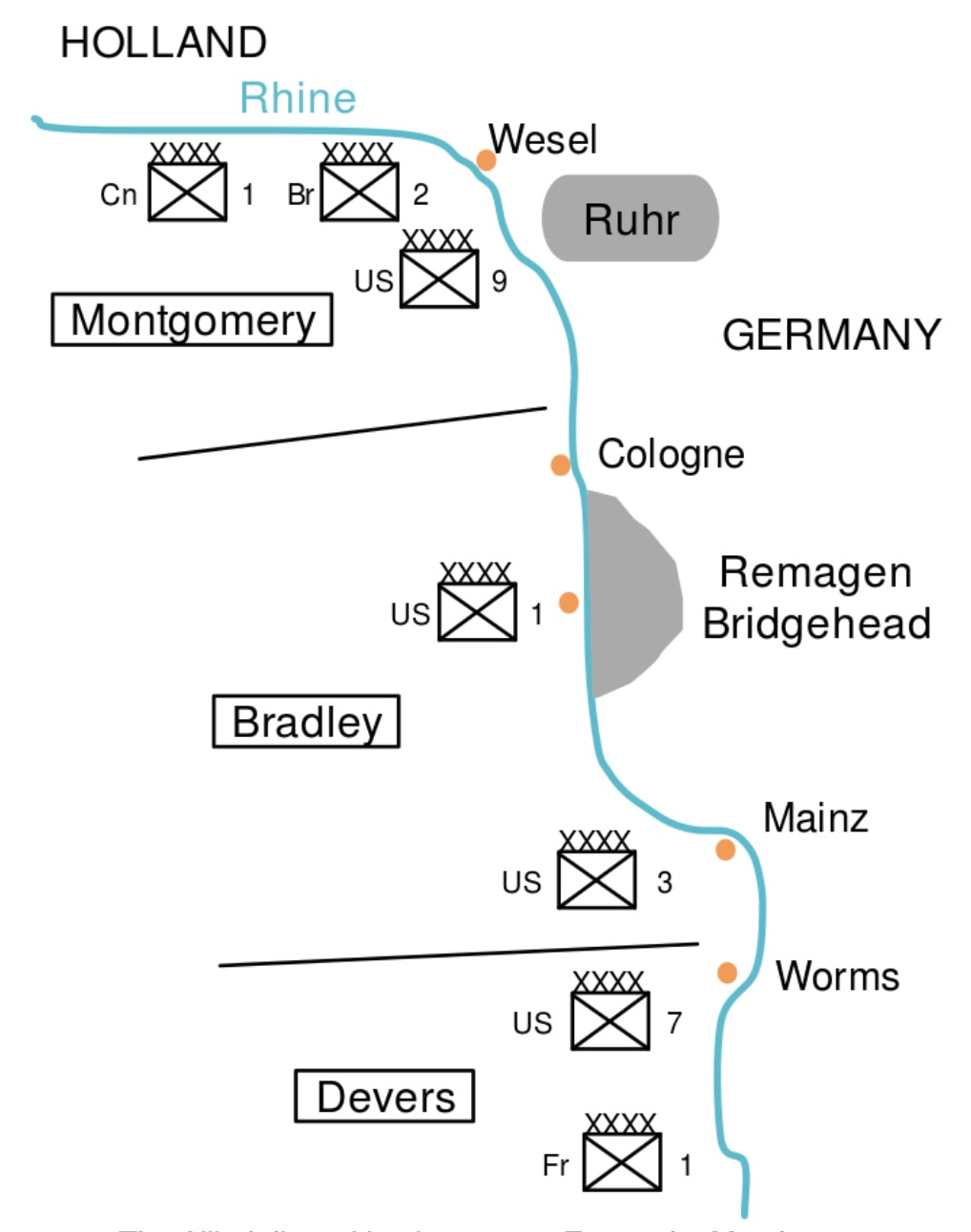
The accompanying schematic map shows the seven Allied armies organized into three army groups as they were situated on 22 Mar 1945, at the end of the Advance to the Rhine.
Here are the first Allied crossings of the Rhine:
|
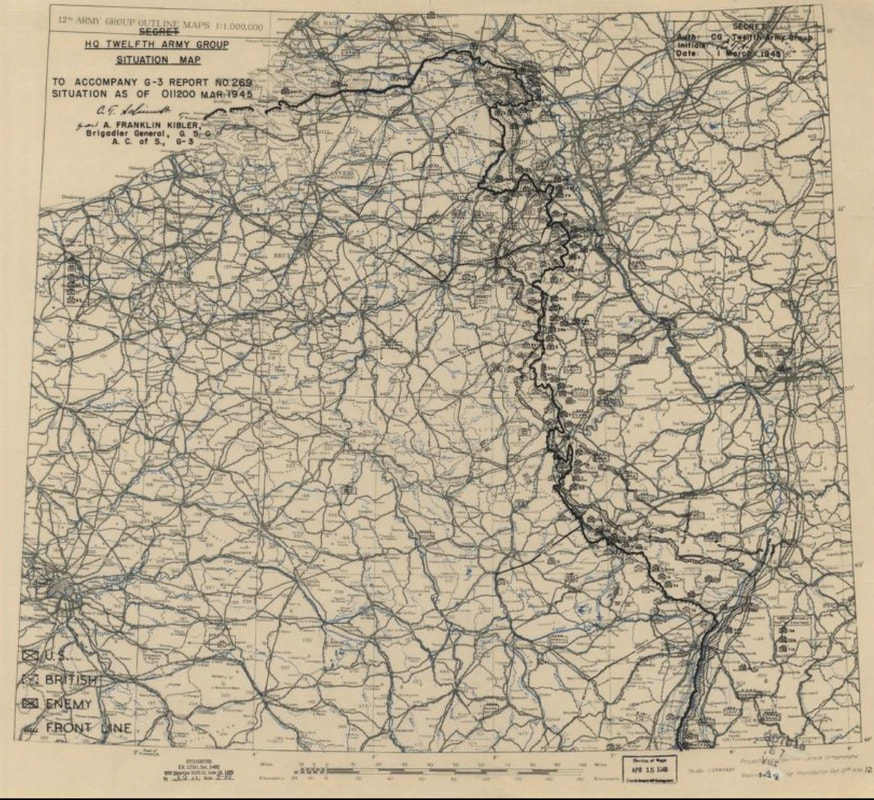
The ETO Situation May, 1 March 1945
|
This is the 12th Army Group's situation map for 1 March 1945.
|
Sources for Big Pigeon's The ETO > To the Rhine 1945 webpage:
Major Sources:
Major Sources:
- None at this time.
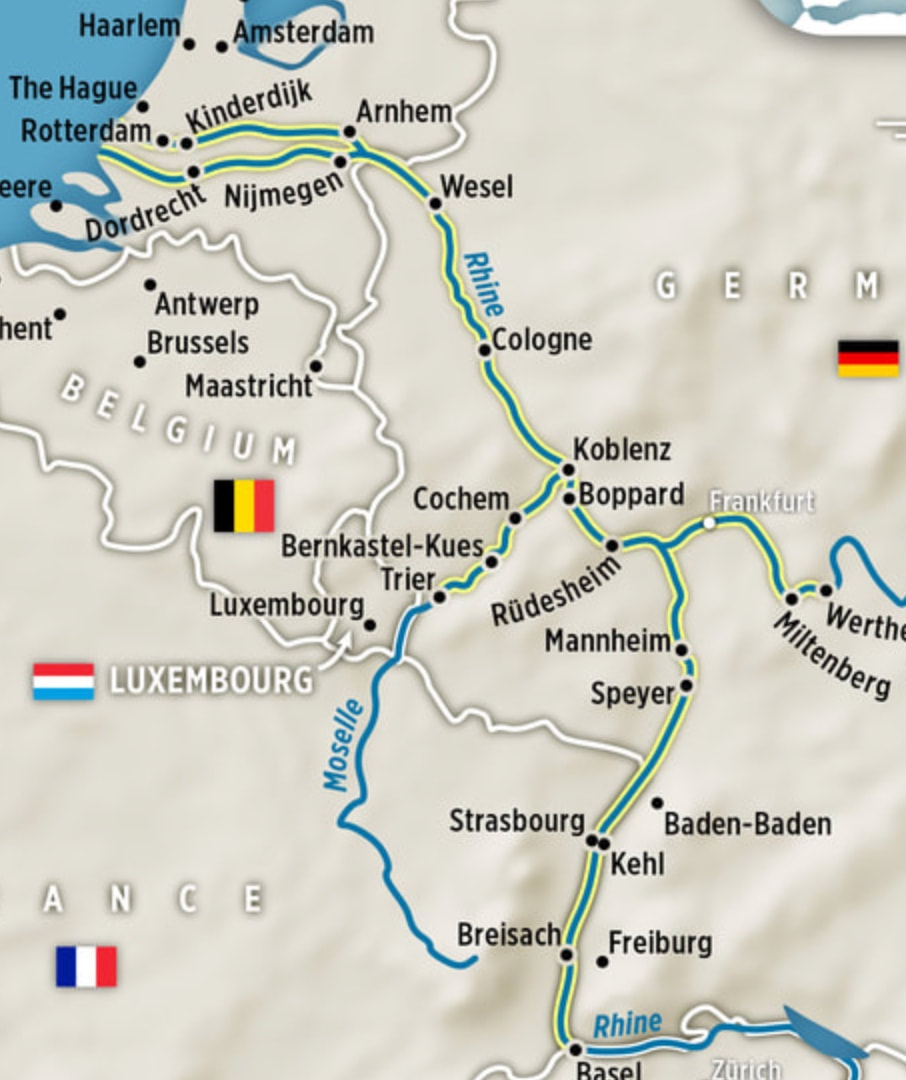
- Rhine River in Germany, map, https://www.authenticvoyages.com/rhine-river-cruises.html - C/O The Luxury Cruise Experts, https://www.authenticvoyages.com.
- ETO Armies at the End of the Rhineland Campaign, map, https://www.warhistoryonline.com/world-war-ii/10-important-facts-about-operation-varsity.html - C/O War History Online, https://www.warhistoryonline.com.
--------- I plan to remove the following later.
By the end of January 1945, Germany forces had been squeezed from the bulge created by the massive Ardennes counteroffensive of December and were again behind the defensive fortifications known as the Siegfried Line or West Wall. Offensive operations, suspended by the Western Allies in mid-December 1944, had already resumed.
General Dwight D. Eisenhower, the ground commander of the Allied Expeditionary Forces in the European Theater, envisaged a two-step approach to taking the war to the German heartland east of the Rhine River.
I have broken the massive winter 1945 campaigns which left the Allied armies at the Rhine into five components:
I propose splitting The Advance to the Rhine - 1945 into two components, 23 Jun 2022
The Siegfried Line - 1945:
Links to subordinate webpages: (to be removed)
By the end of January 1945, Germany forces had been squeezed from the bulge created by the massive Ardennes counteroffensive of December and were again behind the defensive fortifications known as the Siegfried Line or West Wall. Offensive operations, suspended by the Western Allies in mid-December 1944, had already resumed.
General Dwight D. Eisenhower, the ground commander of the Allied Expeditionary Forces in the European Theater, envisaged a two-step approach to taking the war to the German heartland east of the Rhine River.
- First the seven armies under his command would secure the entire west bank of the Rhine.
- Then a massive crossing of the lower Rhine would deposit a large mobile force on the east bank. That force could then race across the north German plain and meet Soviet forces advancing from the east. (If circumstances were favorable, a second and smaller Rhine crossing in the Frankfurt area further south was anticipated.)
- The First Army seized a bridge across the Rhine on 7 March.
- The Third Army crossed the Rhine by boat at multiple locations late in March.
I have broken the massive winter 1945 campaigns which left the Allied armies at the Rhine into five components:
- Alsace, January-March 1945 - The Seventh and First French Armies from 1 January to the middle of March.
- North Rhineland, February-March 1945 - the Ninth and First Armies in February and early March.
- Mid Rhineland, February 1945 - the Third Army.
- Mid Rhineland March 1945 - the First and Third Armies in early March.
- South Rhineland March 1945 - the Seventh and Third Armies in mid and late March.
I propose splitting The Advance to the Rhine - 1945 into two components, 23 Jun 2022
The Siegfried Line - 1945:
- Operation Blackcock, British Second Army (Jan '45)
- The First US Effort, First & Third Armies (late Jan-early Feb '45)
- The Roer River Dams, V Corps, First Army (early Feb '45)
- VIII Corps, Third Army to Prum , (first of Patton's "Probing Attacks, Feb '45)
- XII Corps, Third Army to Bitburg, (first of Patton's "Probing Attacks, Feb '45)
- XX Corps, Third Army to Trier, (third of Patton's "Probing Attacks,Feb '45)
- Alsace, Winter 1945, Seventh & First French Armies (Jan-Mar '45)
- Operation Veritable, Canadian First Army (Feb-Mar '45)
- Operation Grenade, Ninth & First Armies (late Feb-early Mar '45)
- Operation Lumberjack, First & Third Armies (early Mar '45)
- Operation Undertone, Seventh, Third & French First Armies (late Mar '45)
Links to subordinate webpages: (to be removed)
- Ninth & First Armies - during the Rhineland Campaign, advanced to the lower Rhine between Wesel and Remagen.
- Third & Seventh Armies - during the Rhineland Campaign, advanced to the middle Rhine between Coblenz and Mannheim.
|
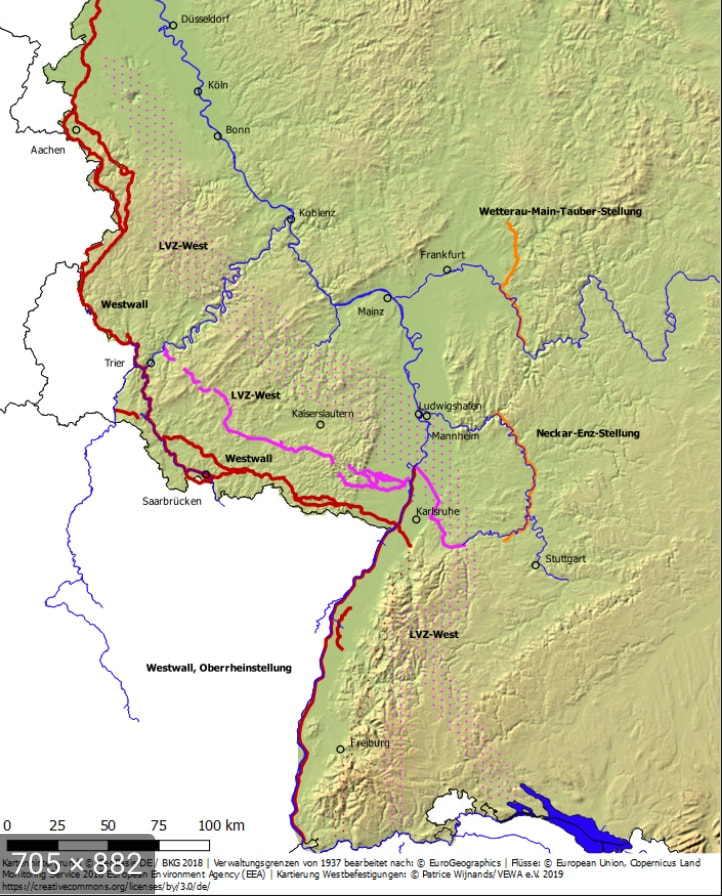
In early February, the western Allies faced two physical obstacles as they began major offensive action eastwards against the Wehrmacht:
At the beginning of February, Allied lines were generally near the Westwall with two exceptions:
ETO's goal in early 1945 was to break through the Siegfried Line and occupy the left bank of the Rhine. This would be followed by a Rhine crossing in the northern Rhineland. |
|
The Rhineland Campaign Overview
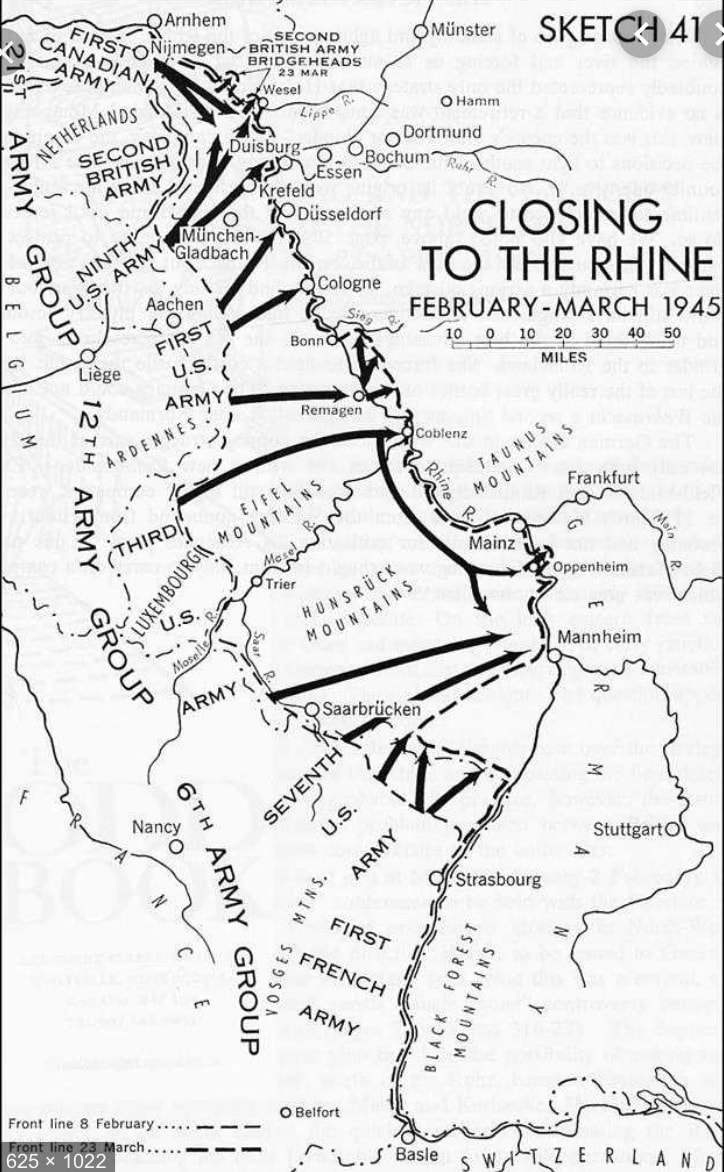
The arrows on the accompanying Canadian map show the major actions of the seven Allied armies during the Advance to the Rhine after 8 February. The heavy dashed line shows the situation on 23 March 1945, with three Rhine crossings already in place. US sources generally use 21 March as the Rhineland Campaign ending date. My report ETO Ground Forces Outline includes the corps that comprised each of the four United States armies during February and March 1945. General Eisenhower preferred to capture all of the Rhine's left bank before attempting a crossing. Crossing plans were based on a massive amphibious and airborne operation in the vicinity of Wesel at the top of the map. Thus the Rhineland Campaign was initially planned with the future Wesel crossing in mind, with priority to Montgomery's 21st Army Group in the north. Bradley's 12th Army Group in the middle was initially cast in a supporting role. Dever's 6th Army Group in the south was recovering from recent battles and did not participate in the Rhineland Campaign until mid March. As the Rhineland Campaign progressed, events caused drastic changes in the original plans. Apropros of this, it was General Eisenhower who passed into common parlance the saying "Plans are worthless, but planning is everything". |
I conceptualize the Rhineland Campaign of 1945 as consisting of three phases. To demark each phase, I've used the date on the accompanying map.
|
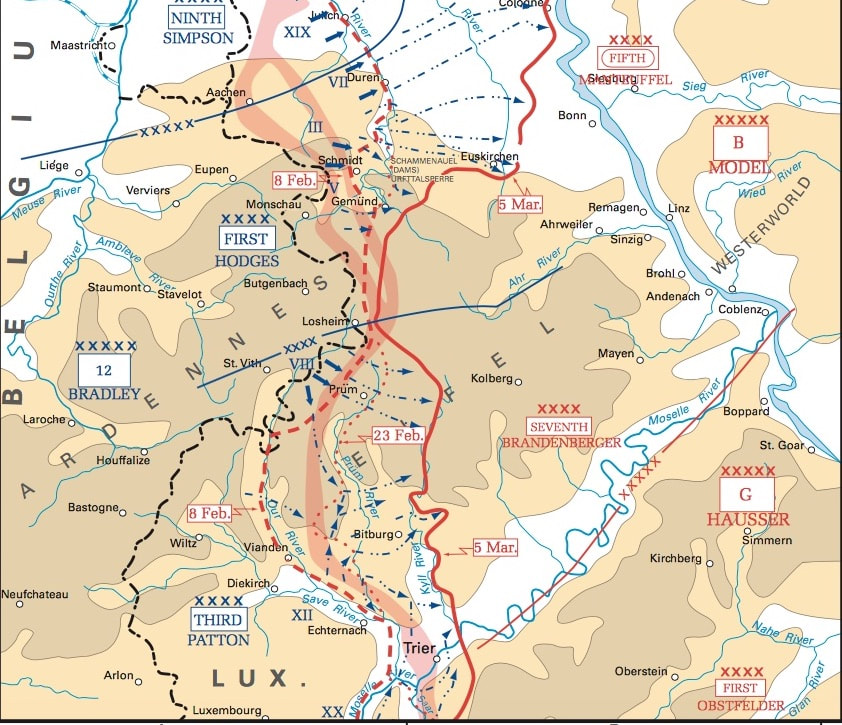
First Phase, 8 Feb - 5 Mar 1945, Advance past the Roer River in the north & the Siegfried Line in the middle.
Summary of US Army major actions:
|
|
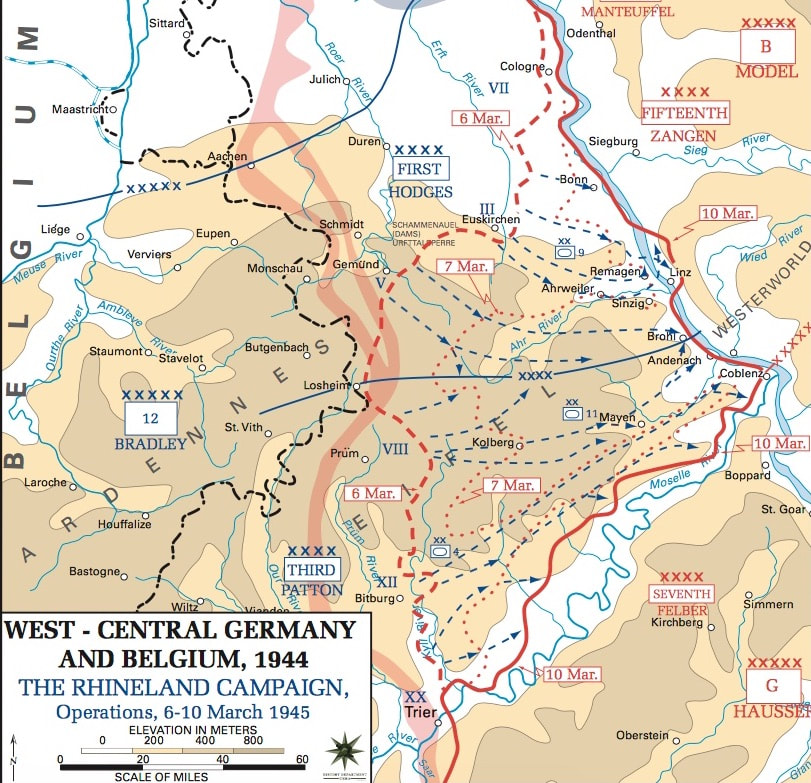
Second Phase, 6 - 10 Mar 1945, Close to the Rhine in the North, breakout in the middle:
|
|
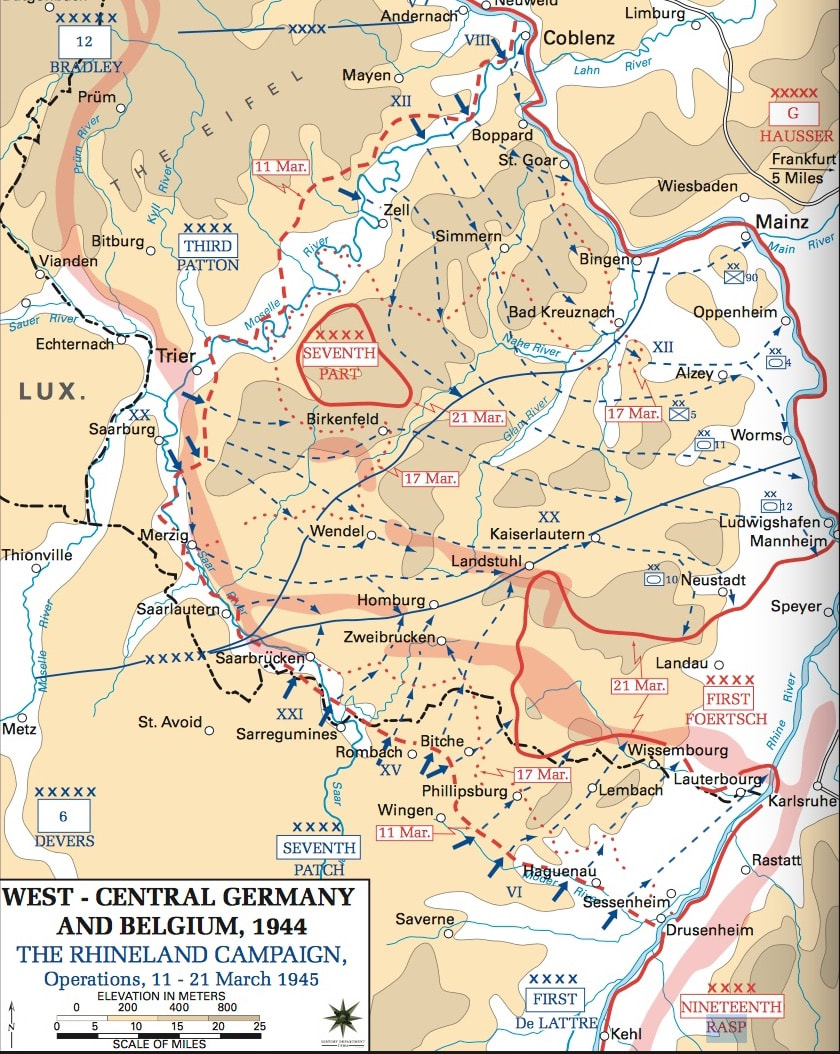
Third Phase, 11-24 Mar 1945, Clear the Palatinate and Saarland in the south:
Ninth Army prepared for the pending Rhine Crossing. First Army prepared for a breakout from the Remagen Bridgehead. Third Army bridged the Moselle River in various locations and raced southeast, both to different Rhine crossing sites and to support the Seventh Army offensive. Seventh Army's offensive , Operation Undertone, began on 15 March. Note on the accompanying map that Seventh Army still had to advance through northeastern Alsace, and then through the Siegfried Line. Considering these difficulties, the Seventh Army turned over additional portions of the Palatinate to the Third Army. The revised army boundary passed through Kaiserslautern as shown on the accompanying map. Operation Undertone, the official Seventh Army offensive, began on 15 March and ended on 24 March. |
|
The Rhineland Campaign Ends
When the Rhineland Campaign officially ended on 21 March 1945, the Western Allies front lines lay on the Rhine River with two exceptions:
In the next two days, two new Allied bridgeheads would appear on the east bank of the Rhine:
The final European Theater campaign of WW II, the Central Europe Campaign, officially began on 22 March 1945. |
Sources for the WW II The ETO > The Advance to the Rhine webpage:
Major Sources:
Major Sources:
- The Last Offensive, https://www.ibiblio.org/hyperwar/USA/USA-E-Last/index.html#index, by Charles B. MacDonald.
- The The Westwall & the Rhine River map is courtesy of https://www.vewa-ev.de.
- The Rhineland Campaign Overview map is courtesy of the Canadian website tothosewhoserved.org.
- The Sixteen German Federal States index map is courtesy of the Nations Online Project. (not being used)
- The Siegfried Line Smashed, Eifel Plateau Overrun, and Palatine Cleared maps are courtesy of the United States Military Academy.
- The End of the Official Rhineland Campaign map is courtesy of the United States Military Academy. I do not believe the death figures in small type are all correct.